Nutritional Content Breakdown: Ginger Ale Nutrition Facts
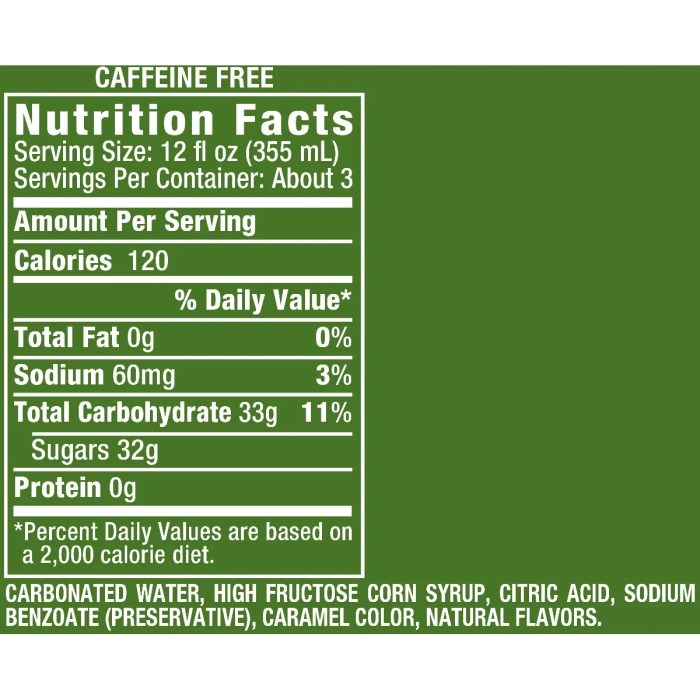
Ginger ale nutrition facts – Understanding the nutritional content of ginger ale is crucial for making informed choices about your beverage consumption. This section provides a detailed comparison of the nutritional profiles of regular and diet ginger ale, highlighting the key differences and the impact of added sugars.
The following table presents a typical nutritional breakdown for a single serving (approximately 8 fluid ounces) of both regular and diet ginger ale. Note that specific values may vary slightly depending on the brand and specific recipe.
Nutritional Comparison of Regular and Diet Ginger Ale
| Nutrient | Regular Ginger Ale | Diet Ginger Ale | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 100-120 | 0-10 | kcal |
| Total Carbohydrate | 25-30 | 0-1 | g |
| Sugars | 24-28 | 0-0.5 | g |
| Protein | 0 | 0 | g |
| Fat | 0 | 0 | g |
| Sodium | 10-20 | 10-20 | mg |
Differences in Nutritional Content
Regular ginger ale typically contains a significant amount of added sugars, which contribute to its caloric content. The sugars primarily come from high-fructose corn syrup or sucrose. Diet ginger ale, on the other hand, utilizes artificial sweeteners to achieve a similar taste profile without the calories and carbohydrates found in its regular counterpart. This results in a drastically reduced caloric intake and carbohydrate content.
The sodium content is usually similar in both versions.
Impact of Added Sugars
The high sugar content in regular ginger ale is a significant factor to consider. Excessive sugar intake is linked to various health issues, including weight gain, type 2 diabetes, and tooth decay. The added sugars provide empty calories, meaning they offer little to no nutritional value beyond energy. By choosing diet ginger ale, consumers can significantly reduce their sugar intake and avoid these potential negative health consequences.
However, it’s important to be mindful of the potential long-term effects of artificial sweeteners, which remain a subject of ongoing research.
Ginger Ale and Health

Ginger ale, while often enjoyed as a refreshing beverage, derives some of its health properties from ginger, a rhizome with a long history of use in traditional medicine. Understanding the potential benefits and drawbacks of this popular drink requires considering both the ginger content and the other ingredients present, particularly sugar and carbonation.
Ginger’s Anti-inflammatory Properties
Ginger contains bioactive compounds, such as gingerols and shogaols, which are responsible for its pungent flavor and possess potent anti-inflammatory effects. These compounds work by inhibiting the production of inflammatory molecules, thus potentially reducing pain and swelling associated with various conditions. Studies have shown that ginger can be beneficial in reducing inflammation related to osteoarthritis and other inflammatory diseases.
However, it’s crucial to remember that the ginger concentration in commercially produced ginger ale is often quite low, limiting the significant impact on overall inflammation compared to consuming fresh ginger directly.
Understanding ginger ale nutrition facts is crucial for those watching their sugar intake. However, a balanced diet considers all aspects, including the nutritional content of other foods like tortillas. For a comparison of carbohydrates and other nutrients, you might find the information on corn tortilla nutrition facts helpful. Returning to ginger ale, remember to check the label for added sugars and sodium, impacting your overall nutritional profile.
Potential Negative Health Effects of Excessive Consumption, Ginger ale nutrition facts
While moderate consumption of ginger ale is unlikely to cause harm for most people, excessive intake can pose several potential health risks. The high sugar content in many commercially available brands contributes to weight gain, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. Furthermore, the carbonation can cause bloating and gas in some individuals. The acidity of ginger ale, while generally mild, could exacerbate existing gastrointestinal issues in sensitive individuals.
For example, someone with acid reflux might experience worsened symptoms after consuming large quantities. Therefore, moderation is key.
Nutritional Comparison to Other Carbonated Beverages
Compared to other carbonated beverages like cola or other sugary sodas, ginger ale generally offers a slightly better nutritional profile. While still high in sugar, it may contain small amounts of ginger, offering some additional health benefits, however minimal. However, this advantage is often negligible when compared to healthier alternatives such as water, unsweetened tea, or even naturally flavored sparkling water.
Many ginger ales lack significant vitamins or minerals, making them a less nutritious choice than beverages rich in essential nutrients. For instance, a typical serving of orange juice provides a significant amount of Vitamin C, whereas a comparable serving of ginger ale provides almost none.
Ingredient Analysis
Understanding the ingredients in ginger ale is crucial to appreciating its flavor profile and potential health impacts. The interplay of these components significantly influences the final product, from its sweetness and spiciness to its overall nutritional value. This section will delve into the role of key ingredients and explore the implications of artificial additives commonly found in commercially produced versions.
Ginger, the namesake ingredient, provides the characteristic pungent, spicy flavor and aroma. Its bioactive compounds contribute to the drink’s potential health benefits, although the concentration in ginger ale can vary significantly depending on the brand and manufacturing process. Sugar, typically high-fructose corn syrup or sucrose, contributes the sweetness and body to the beverage, but is also a major source of calories and can negatively impact blood sugar levels.
Carbonation, achieved through the addition of carbon dioxide, provides the effervescence and refreshing fizz that defines the ginger ale experience. It also affects the mouthfeel and perceived intensity of the flavor.
Artificial Sweeteners and Preservatives
The use of artificial sweeteners and preservatives in commercially produced ginger ales raises concerns about potential long-term health effects. Artificial sweeteners like aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin are used to reduce the sugar content and calorie count, but some studies suggest possible links to various health issues, although the evidence remains inconclusive and often debated. Preservatives, such as sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate, are added to extend shelf life and prevent microbial growth.
However, some individuals may experience adverse reactions, such as headaches or allergic responses, to these additives. The long-term effects of regular consumption of these artificial ingredients are still under investigation and require further research.
Comparison of Ingredients in Popular Brands
A comparison of several popular ginger ale brands reveals significant differences in their ingredient lists. This highlights the importance of checking labels and making informed choices based on individual dietary needs and preferences.
The following table illustrates a simplified comparison, focusing on key ingredients. Note that formulations can change, so it is always recommended to check the most current product labeling. This is a simplified example and does not represent an exhaustive list of all brands or all ingredients.
| Brand | Sweetener | Preservatives | Other Notable Ingredients |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | High-fructose corn syrup | Sodium benzoate | Natural flavors, citric acid |
| Brand B | Sugar | Potassium sorbate | Ginger extract, caramel color |
| Brand C | Sucrose, artificial sweetener (e.g., sucralose) | None listed | Natural flavors, carbonated water |
FAQ Corner
Is ginger ale good for digestion?
Ginger has properties that may aid digestion for some individuals, but the high sugar content in many ginger ales can counteract this benefit.
Does ginger ale contain caffeine?
Most ginger ales do not contain caffeine. However, always check the specific product label to be sure.
Are there low-sugar or sugar-free options available?
Yes, many brands offer diet or low-sugar versions of ginger ale sweetened with artificial sweeteners.
Can ginger ale cause tooth decay?
The acidity and sugar content in many ginger ales can contribute to tooth decay if consumed excessively. Rinsing your mouth with water after consumption can help mitigate this risk.
What are the best brands of ginger ale in terms of nutritional content?
This varies based on individual preferences and nutritional goals. Comparing nutrition labels from various brands allows consumers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs.